$5 Trillion Metaverse Harvest by 2030. African Startups Should Gear up for the Biggest Pie

The Metaverse will become the most user-friendly tech when it finally goes past its current relatively nascent state. It is user-friendly because by definition and operability, the Metaverse is the next iteration of the internet that seamlessly combines our digital and physical and social lives. What exactly is the Metaverse? A gaming platform; a virtual retail destination; a training tool, an advertising channel; a digital classroom; a new gateway to digital experiences. One can rightly assert that the tech will function as all of the above; it will be what we make it.
“We have Instagram; email; messaging. And then there’s our real-life friends; the real-life activity that we’re participating in. Sometimes there’s an intersection between those two. But when I think about a real-world vision of the Metaverse, it’s really a union of those where they become much more deeply fused; where there’s a digital extension to everything that’s real.” –John Hanke, CEO of Niantic.
Mark Zuckerberg—the Meta Lord, said last November as he announced that the Metaverse will be the successor to the mobile internet. As bold as this sounds, history has taught us no to undermine the possibilities that accompanies tech. As at 1992, all mobile phones still had buttons, the iPhone didn’t appear until 15 years later, and the iPad was still 18 years away. Today we can take these advancements that seemed impossible for granted, because sophistications keep coming up.
While estimates of the potential economic value of the Metaverse vary widely, a view of consumer and enterprise use cases suggests it may generate up to $5 trillion in impact by 2030— equivalent to the size of the world’s third-largest economy today, Japan.
A $5 Trillion Metaverse Harvest
It was predicted that up to $10 billion had already been invested on artificial intelligence a few years ago. Right now, it stands at $93 billion. According to McKinsey Insights, there is an expected exponential increase in the Metaverse’s economic worth. This is because consumers are willing to spend money on digital assets because of its appeal across genders, geographic regions, and generations.
McKinsey Insights also noted that individuals are receptive to new technologies, businesses are substantially investing in the creation of Metaverse infrastructure, and brands that have been experimenting with the Metaverse are reporting back. ‘The potential economic worth of the Metaverse as a whole is significant given this.’
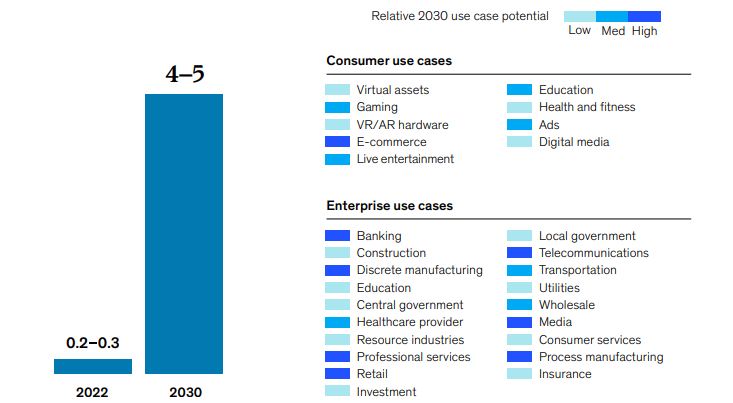
Given the scope of potential applications and uses as well as the level of investment from major technological companies, venture capital, corporations, and brands, the metaverse is also projected to be the largest new growth opportunity for a number of industries in the ensuing decade. Industries are already putting metaverse projects into practice, albeit most of the focus to date has been on marketing.
Everyone, from business owners to investors, requires at least a basic understanding of how the Metaverse functions in order to function efficiently in daily life and to take full advantage of the opportunities it provides.
Although the various components of the metaverse are yet to enjoy wide acceptance across Africa, metaverse growth projections released on May 16 by Analysis Group, a research company contracted by Meta, indicate that the metaverse will pump an additional $40 billion into sub-Saharan Africa’s gross domestic product (GDP) in the next ten years.
The Rest of the World
South Korea became the first government to join the Metaverse. Administrators in South Korea’s capital, Seoul, announced a five-year “Metaverse Seoul Basic Plan” that will begin by creating a virtual Seoul City Hall, plaza, and civil-service center.
Jong-Soo Park, CIO of Seoul’s Smart City Policy Bureau, opined that the aim was to provide civic freedom, participation, engagement, and communication for citizens.
“We believe that with the Metaverse we can create higher-quality government services,” he said. “Current government services are demand driven. However, we believe that in the future we can provide services in advance of demand—we can provide a new form of government services and, in that sense, it will be very helpful to citizens. We also believe this Metaverse platform will help citizens see Seoul city in a different perspective,” said Park.
Despite the buzz, the Metaverse is still developing as stakeholders have been increased in width and sizes. Since its introduction in 2006, Roblox has attracted businesses like Nike and Gucci as partners and advertisers. More than 27 million unique players attended a Travis Scott performance last April 24, and Fortnite has more than 20 million daily active users (DAUs), hosted concerts, and has produced more than $14 billion in transactions between its users between 2018 and 2020. With more than 300 million users worldwide, Zepeto by Naver Z, Asia’s biggest Metaverse platform, teamed up with Samsung in April for its Galaxy S22 Treasure Hunt campaign.
An unknown customer reportedly spent $450,000 for a piece of virtual land in The Sandbox close to Snoop Dogg’s virtual home, “Snoopverse,” putting virtual real estate in the spotlight as well. The list of Metaverse platforms and investors continues to grow and diversify.
African Startups and the $5 Trillion Metaverse Harvest
Startups can engage in and profit from the Metaverse in a variety of ways. From creating and managing a private digital world and platform, to offering goods and services to Metaverse users, to developing hardware and software. However, articulating your Metaverse goals is only the first step in formulating a stance.
Customers are gravitating toward the Metaverse, therefore it’s crucial to analyze how it may affect your business both favorably and adversely and develop a strategy. Not engaging in the Metaverse could put the business at a big competitive disadvantage. The Metaverse is likely to have an impact on how organizations run as well as how they engage with customers. New methods for learning, development, and recruiting will be available to human resources.
The Metaverse’s potential is already being used in marketing. Users are already organizing events, host them, go to them, and engage in discussions and negotiations. The Metaverse can be used by customer service to conduct service calls or to show customers how to do things. New design tools and the utilization of digital twins will speed up research and development. For general and administrative activities, the Metaverse could be used by the operations function as well.
By 2030, it is entirely plausible that more than 50% of live events could be held in the Metaverse. More than 80% of commerce could be impacted by something consumers do there, from discovering brands to visiting a virtual store. The Metaverse could become the biggest pie open for startups.
