Deep Diving Into the Tanzanian Tech Startup Ecosystem

The Tanzanian tech startup ecosystem has undergone tremendous growth and development over the past decade. In the early days, the startup scene was small, with only a few entrepreneurs taking advantage of the opportunities presented by technology. However, over the years, the number of startups and investment in the sector has increased significantly, now boasting hundreds of startups.
The East African country with a population of 64 million, GDP of $67.48 billion, and internet penetration rate of about 50% of the nation’s population was ranked at number 114 on the global Startup Ecosystem, with Dar es Salaam, as its commercial headquarter ranked at 583 globally according to StartupBlink Map.
In the early 2010s, there were only a handful of tech startups in Tanzania. However, over the past few years, the number of startups has increased dramatically, and the ecosystem has matured. One of the main drivers of this growth has been the increasing availability of internet connectivity, as well as the growth of mobile technology. The widespread use of mobile phones and the growth of mobile networks have made it easier for entrepreneurs to start and grow their businesses.
Tanzanian Startup Funding
Additionally, in terms of venture capitalists’ activities in the sub-region, the Eastern African region has been showing great promise over the years, only coming second to West Africa in 2022. Also, the region has secured over $3.5 billion, which represents about a quarter of the total funding raised by African startups since 2019, with the vast majority of the funding raised in the region going to Kenya: with total funding since 2019 nearing $3 billion. However, of the 10 $50m+ deals recorded in Eastern Africa since 2019, 9 were in Kenya (the only outlier is Tanzania’s Zola Electric’s $90m round of September 2021). Tanzania along with Uganda are the only other two markets to have attracted more than $100m in total funding since 2019, according to the Big Deal Report.
Also, the Tanzanian tech startup which ranks #8 in the continent has been representing in terms of funding in recent time, raising $80 million (-16% YoY) through 11 deals in 2022, which fall short of its 2021, $96 million funding record.
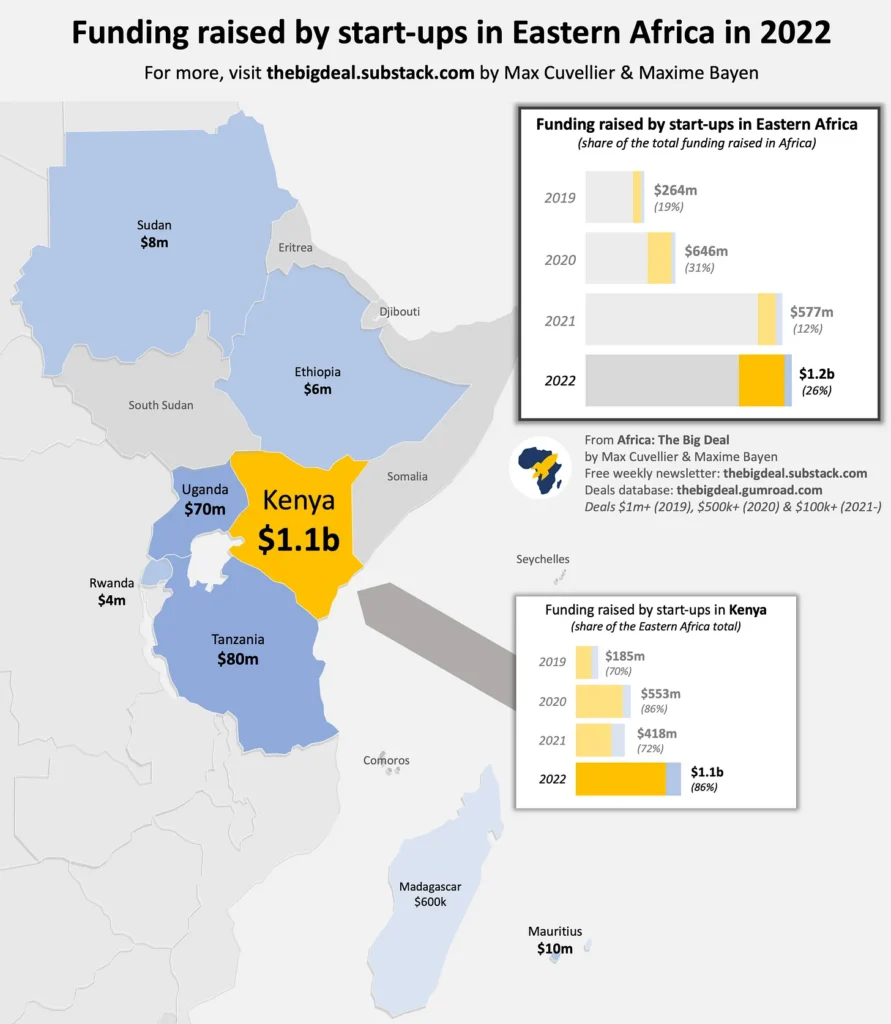
Source: The Big Deal
One of the key areas in which the Tanzanian tech startup ecosystem has grown in the fintech sector. In the early days, fintech startups focused primarily on mobile money services, but today, the sector has expanded to include other areas such as insurance, lending, and investment management. One of the most notable fintech startups in Tanzania is Tigo Pesa, which has become one of the leading mobile money services in the country. Other notable fintech startups include Bima and Branch, both of which have raised significant investment from international investors.
The e-commerce sector is another area where the Tanzanian tech startup ecosystem has grown. A variety of factors have contributed to the growth of e-commerce in Tanzania, including increased internet use, a growing middle class, and increased mobile phone use. Several e-commerce startups have emerged in Tanzania in recent years, including Jumia, Kilimall, and MallforAfrica. Aside from these sectors, there has been growth in others such as agritech, healthtech, and edtech. Agritech startups, for example, have focused on using technology to increase agricultural efficiency and make it easier for farmers to access information and resources.
Some Leading Tech Startups in Tanzania
Sheria Kiganjani is a shining example of how startups are thriving in Tanzania. The online legal digital platform “enables people to access various legal services, and materials, and connects people with nearby advocates. An end-user can use his mobile phone to access various legal articles, materials, news, reported cases, Acts, legal documents, and information.” Sheria Kiganjani was named the Seedstars Dar Es Salaam competition winner in 2019.
Silabu, a digital platform connecting students to qualified and certified private tutors online and offline, is another leading tech startup in the country. It is Tanzania’s leading marketplace for flexible and on-demand tutoring services. E-Motion designs and manufactures electric safari vehicles for tour operators in the sustainable tourism industry. They can also convert your old gasoline car into a brand-new electric vehicle. Tunzaa is an Africa-focused marketplace that sells goods and services online to low and middle-income earners. Dawn Mkononi is a pharmaceutical supply and e-commerce platform for pharmacies and healthcare facilities. Neurotech creates layer-one infrastructure for developers to implement industry-ready natural language processing solutions for African languages. CutOff Recycle converts human hair waste into effective fertilizers and pesticides for arable farming. It also creates hair fiber reinforcement technology to strengthen construction bricks.
Government Support and reasons to Choose Tanzania
The Tanzanian tech startup ecosystem has also benefited from several initiatives and programs aimed at fostering startup growth over the last decade. For example, the government has implemented several tax breaks for startups, which has aided in attracting investment in the sector. Furthermore, several accelerators and incubators have been established in the country, providing support and resources to startups.
Tanzania aims to become a middle-income economy by 2030 through aggressive industrialization. Dar Es Salam, Tanzania’s commercial hub, should achieve “megacity” status by the same year.
With a projected population of 10 million, it will be a desirable consumer base for tech entrepreneurs. Companies that are already established in the area will benefit greatly from being the first to move.
According to Sahara Ventures Founder, Jumanne Rajabu Mtambalike “Tanzania’s innovation ecosystem is among the most diverse [with] Data Labs, Arts Spaces, Living Labs, Community Spaces, maker spaces, Creative Spaces, Incubators, Accelerators, and Technology Hubs [who] are distributed across the country even in extremely rural areas.”
Two-thirds of Tanzania’s population is under the age of 25. Teenagers are the most valuable customers in technology because they lack brand preferences and are early adopters.
Economic and Political Environment
Tanzania has good macroeconomic policies, a stable political environment, and structural reforms, and is resilient to external shocks. As a result, the country has maintained consistent GDP growth of 6 to 7% per year since the end of the 1990s, making it one of Africa’s fastest-growing economies.
Tanzania Investment Center serves as a one-stop shop for business permits, licenses, and approvals.
Strategic Geographic Position
Tanzania is actively involved in cross-border activities and projects like the Ethiopia-Kenya Power Interconnector and the Zambia-Tanzania-Kenya Power Interconnector. These massive Power Pools will expand the regional electricity market.
Dar es Salaam is an international port with connections to the Middle and Far East, Europe, Australia, and America. Malawi, Zambia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Burundi, Rwanda, and Uganda are also served.
Tanzania has numerous airports, the most important of which are Dar es Salaam International Airport, Kilimanjaro International Airport, and Zanzibar Airport. Several international airlines offer direct flights to Tanzania, while the national airline, Air Tanzania, operates domestic and international routes to Zambia, South Africa, India, and China.
Ecosystem Players
Tanzania’s startup ecosystem has a variety of stakeholders that offer non-financial business support, mentoring, and co-working spaces. Key ecosystem players located in this market include Sahara Ventures, Seedstars Dar Es Salaam, Robotech Labs, Vodacom Digital Accelerator, and Innovate Hub.
Investors
For financial investments— smart money for startup growth in Tanzania, entrepreneurs have access to grants, angel investors, pre-seed, debt, and equity investment. Some of them include AHL Venture Partners, Atraxx Group, Beyond Capital Fund, TBL Mirror Fund, and Lundin Foundation.
In conclusion, the Tanzanian tech startup ecosystem has undergone tremendous growth and development over the past decade. From a small and relatively underdeveloped ecosystem, it has grown into a mature and thriving ecosystem, with several successful startups and a supportive environment for entrepreneurship. The future of the Tanzanian tech startup ecosystem looks bright, and we will likely continue to see growth and development in the years to come.
