Digital Payments Reign Supreme in Africa as Mobile Transactions Surge by +22%

Africa has recently emerged as a central hub for the ongoing digital revolution. Digital payments in the region alone accounted for roughly two-thirds of global value in 2022. According to the State of the Industry Report on Mobile Money 2023, the value of mobile transactions in 2022 reached a staggering $1.26 trillion, with Africa playing a significant role in this growth. Many people are wondering what the implications of the surge in mobile money transactions are. The factors driving its expansion, as well as the potential it holds for financial inclusion and African economic development.
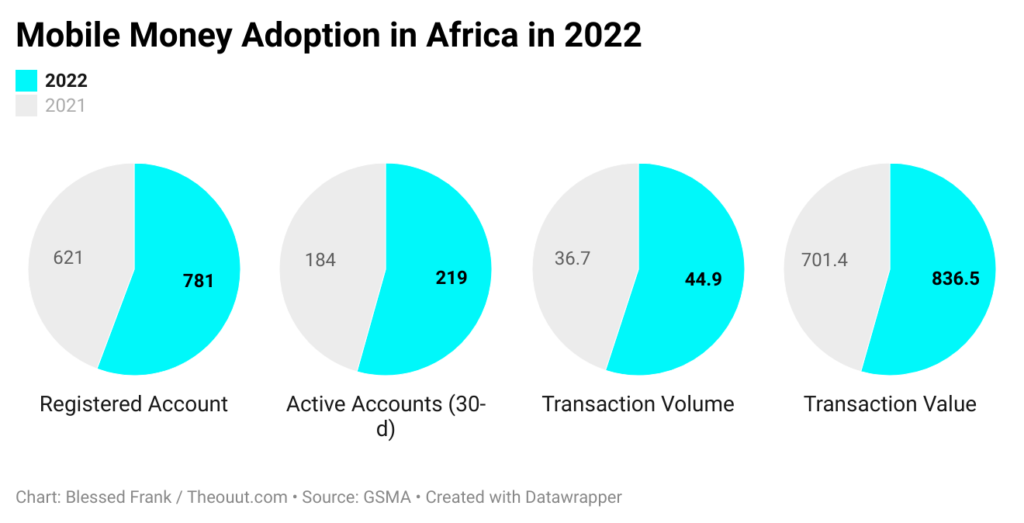
Africa’s mobile money market is rapidly growing. In 2022, there were 781 million registered accounts, 219 million 30-day active accounts, $44.9 billion in transaction volume, and $836.5 billion in transaction value. This represents a 39% increase from the $495 billion processed in 2020, a 21% increase in volume, and a 22% increase in transaction value in 2021. That equates to 173 active services, 621 million registered accounts, 184 million active accounts, $36.7 billion in transaction volume, and $701.4 billion in transaction value. Increased mobile phone penetration, a young and tech-savvy population, a strong desire for digital services across B2B, P2P, and B2C domains, as well as the government’s efforts to embrace a cashless economy, are driving this growth.
The Report Equally Broke Down the Data by Regions
East Africa contributed 59 live services, 296 million registered accounts, 102 million active accounts, $24 billion in transaction volume, and $403.4 billion in transaction value.
West Africa contributed 69 live services, 237 million registered accounts, 58 million active accounts, $9.3 billion in transaction volume, and $239.3 billion in transaction value.
Central Africa contributed 19 live services, and 60 million registered accounts, 19 million active accounts, $2.9 billion in transaction volume and $50.1 billion in transaction value.
Southern Africa contributed 14 live services, 13 million registered accounts, 4 million active accounts, $335 million in transaction volume and $4.9 billion in transaction value.
Northern Africa contributed 12 live services, 15 million registered accounts, 1 million active accounts, $77 million in transaction volume and $3.7 billion in transaction value.
Aside from increased activity in the fintech sector, particularly in the payment vertical, over the last five years, the COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst for the accelerated adoption of electronic payment options in Africa. The desire for contactless payments for everyday items, bill payments, and financial assistance drove people to embrace digital transactions. Mobile money provided a simple and secure way to transfer funds to family and friends, reinforcing the habit of using digital payments even after the pandemic had passed.
Furthermore, regulatory changes in large markets such as Nigeria, Egypt, Kenya, and South Africa have played an important role in driving digital payment growth. The emergence of numerous mobile money players has resulted in an astronomical increase in the number of registered agents as a result of new licenses. This not only created jobs, but also made mobile money services more accessible to a larger population. Other countries have seen similar regulatory shifts, paving the way for increased market competition and innovation.
How Increase Digital Payments Adoption Will Benefit Africa
Mobile money adoption has the potential to transform Africa, a continent marked by a large unbanked population and limited access to financial services. Mobile money can address numerous challenges and open up new opportunities for economic growth and development by allowing individuals to conduct digital transactions using their mobile phones.
First of all, greater mobile money adoption will improve financial inclusion in Africa. A sizable portion of the population, particularly those living in rural areas, lacks access to traditional banking services. Mobile money platforms, on the other hand, provide a convenient and accessible alternative. Mobile money bridges the gap between the unbanked population and financial services by allowing users to store and transfer money digitally, allowing them to participate in the formal economy. As more people gain the ability to save, invest, and engage in productive activities, this inclusion fosters economic empowerment, reduces poverty, and drives economic growth.
Secondly, the use of mobile money can promote secure and efficient transactions. Cash remains the dominant form of payment in many parts of Africa, posing several risks such as theft, loss, and counterfeit currency. Mobile money provides a secure platform for financial transactions, lowering risks and improving overall security. Furthermore, digital transactions can be completed quickly and easily, removing the need for physical travel and the lengthy wait times associated with traditional banking services. This efficiency is especially important for small businesses and entrepreneurs because it allows them to streamline their operations, obtain credit, and expand their customer base.
Economic Stimulant
Moreover, mobile money adoption has the potential to stimulate economic development and drive innovation. By digitalising financial transactions, mobile money platforms generate vast amounts of data that can be leveraged for market research and analytics. This data can inform decision-making, facilitate targeted interventions, and spur entrepreneurship. With a better understanding of consumer behavior and market dynamics, businesses can develop tailored products and services, driving economic diversification and innovation. Furthermore, mobile money platforms can serve as a catalyst for the growth of complementary industries such as e-commerce, digital payments, and mobile-based services, creating new employment opportunities and expanding the digital ecosystem.
Additionally, mobile money adoption can contribute to improved governance and social development. Traditional cash-based systems are often associated with corruption, tax evasion, and informal economies. Mobile money, on the other hand, offers transparency, accountability, and traceability in financial transactions. This increased visibility can help governments combat corruption, improve tax collection, and ensure that resources are directed towards essential services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure development. Furthermore, mobile money platforms can facilitate the delivery of social welfare programs, enabling governments to disburse payments directly to beneficiaries, ensuring greater efficiency, and reducing leakages.
While the growth of mobile money is encouraging, it is critical to recognize that challenges remain. The gender disparity in mobile phone ownership and access to mobile money accounts continues to be a source of concern. To address this disparity, efforts should be directed toward empowering women, improving their digital skills, and increasing their knowledge of mobile financial services. Mobile money can truly realize its potential as a tool for economic empowerment and poverty reduction if inclusivity is ensured.
